[translations idioma=”ES” url=”https://archives.rgnn.org/2015/02/18/como-citar-fuentes-y-anadir-enlaces/”]
ROOSTERGNN is a non-profit news agency that promotes freedom of expression and independent journalism. The ROOSTERGNN Journalism Toolbox is an interactive list of resources for journalists and media professionals, aiding them in becoming better communicators.
In journalism, the customary practice for citing sources is called “attribution”.
WHEN TO CITE
Steve Buttry hits the nails on the head in his article “You can quote me on that: Advice on attribution for journalists,” stating that journalists should cite, or attribute…
- any time that attribution strengthens the credibility of a story.
- any time you are using someone else’s words.
- when you are reporting information gathered by other journalists.
- when you are not certain of facts.
- when you are citing an opinion.
“When you wonder whether you should attribute, you probably should attribute in some fashion,” writes Buttry.
As he explains, information considered to be in the public domain, such as that President Obama likes Basketball, does not need to be cited.

Helping students avoid plagiarism | via Pinterest
BEFORE YOU EVEN CITE
Given how easy it is to copy and paste on the web, always ask yourself the following before you even start citing a source:
- Is the source legitimate? Is it an official news outlet? If not, who is behind the source you are citing?
- If you are using statistics, where are they coming from? How many people were interviewed?
- Please do not cite from Wikipedia. Instead, scroll to the bottom of the Wikipedia article and find the real source that is behind the facts.
- The same goes for any other sources. Check if they are recycling content from other sources, or whether they are the first source that published the quote or data you are going to use.
HOW TO CITE
- Where? Where did your information appear? In The New York Times? From the Census Bureau?
- What? Are you citing a particular article, study or statistic?
- Who? Is there an author of the article? Who said the quote? If you are citing a person that you yourself did not interview, cite the origin of the interview. Please differentiate between press releases and news articles.
- When? When did your information appear?

Keep calm and use textual evidence | via Pinterest
LINKS, LINKS, LINKS
Link to the actual source. You can link to a website, an image (such as a graph), to a video, PDF or any kind of other file.
Highlight some text and clickon the “Insert link” button, as shown below, when you are uploading content to ROOSTERGNN.
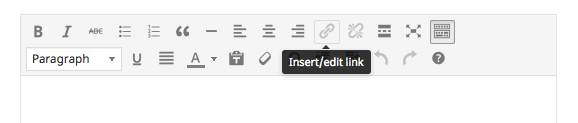
Insert a link when uploading articles to ROOSTERGNN (make sure your text to link is highlighted)
A pop-up window will apear for you to add your link. Include the URL and the link title, and select “open link in a new window/tab”.
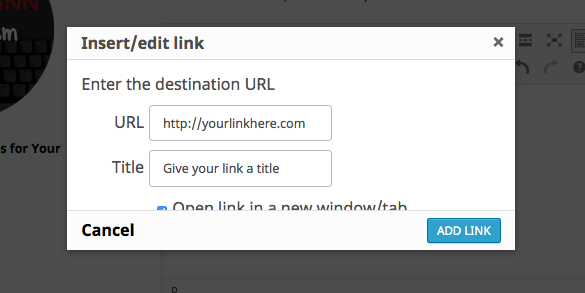
Insert your link and title
If you made a mistake and would like to remove the link, just highlight the text again and click on the “remove link” button.
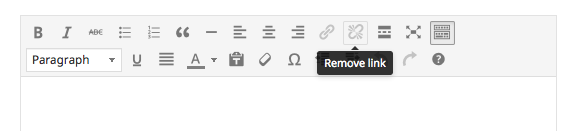
Removing links
A NOTE ON FOOTNOTES
Universities teach students how to cite sources for academic articles, frequently in the form of a bibliography at the end of an article, or footnotes throughout the article.
However, when writing journalistic articles for the web, or even in print, it is not customary to use neither footnotes, nor to cite an entire bibliography at the end.
At ROOSTERGNN, we generally do not use footnotes or bibliographies.
If you really need to, you can include a box at the end of the article to cite a list of sources. However, keep in mind that on the web, this usually disrupts the narrative and it is better to cite in-line using links.